Setting Goals
Two of the more popular methods for setting goals are SMART and CLEAR:
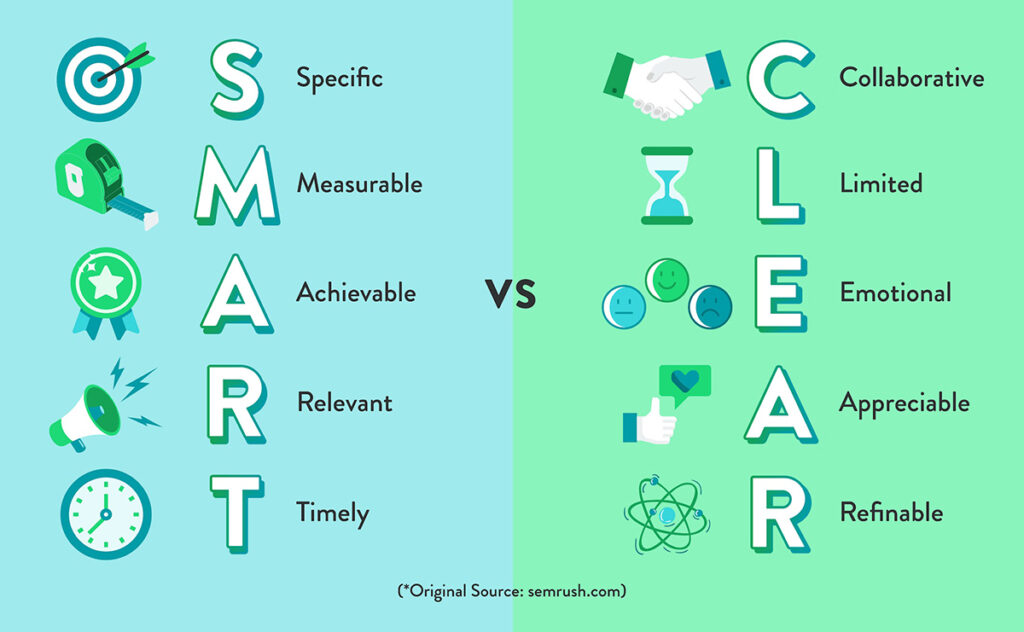
SMART Goals
This method helps ensure that the goals have been thoroughly vetted. It also provides a way to clearly understand the implications of the goal-setting process.
Specific – To set specific goals, answer the following questions: who, what, where, when, which, and why.
Measurable – Create criteria that you can use to measure the success of a goal.
Attainable – Identify the most important goals and what it will take to achieve them.
Realistic – You should be willing and able to work toward a particular goal.
Timely – Create a timeframe to achieve the goal.
For more information about S.M.A.R.T. goals, read “The Essential Guide to Writing S.M.A.R.T. Goals.”
CLEAR Goals
A newer method for setting goals that takes into consideration the environment of today’s fast-paced businesses.
Collaborative – The goal should encourage employees to work together.
Limited – They should be limited in scope and time to keep it manageable.
Emotional – Goals should tap into the passion of employees and be something they can form an emotional connection to. This can optimize the quality of work.
Appreciable – Break larger goals into smaller tasks that can be quickly achieved.
Refinable – As new situations arise, be flexible and refine goals as needed.
During this phase, the scope of the project is defined and a project plan is developed. It involves identifying the quality of the work, available resources, and a realistic timetable. The project plans also includes establishing baselines or performance measures. These are generated using the scope and schedule of a project. A baseline is essential to determine if a project is on track.
At this time, roles and responsibilities are clearly defined, so everyone involved knows what they are accountable for.
